PUBLICATIONS WITH ABSTRACTS
PUBLIKáCIóS LISTA KIVONATOKKAL
If Symbol font is not available, Greek characters, arrows and
other special characters are not displayed correctly on your screen. For the pdf files you need Acrobat Reader, freely downloadable from Adobe.
Ha a Symbol karakterkészlet nem érhetõ el az ön által használt számítógépen, a görög karakterek, nyilak és más speciális jelek nem láthatók jól a képernyõn. A pdf fájlok megtekintéséhez az Adobe cégtõl ingyenesen letölthetõ Acrobat Reader-re van szükség. A közlemények kivonatai - egyelõre - csak angolul hozzáférhetõk.
2005
Abstract: Guanine derivatives substituted at N7 with different benzyl groups (benzyl, 4-methoxybenzyl, 4-nitrobenzyl) have been evaluated in the regioselective N9-alkylation of guanine. Given the capricious removal of (substituted) benzyl groups from guanine derivatives an improved alternative approach has been elaborated consisting of the sequence pent-4-enoylation of guanosine at N2 (6), per-O-acetylation (8), 4-nitrobenzylation at N7 followed by N-glycoside hydrolysis (10), N9-alkylation (13) and deprotection with sodium dithionite to afford the PNA building block tert-butyl [N2-(pent-4-enoyl)guanin-9-yl]acetate (15) in 36% overall yield without N7 regioisomer formation, solubility problems and chromatographic purification. A remarkable influence of the O- and/or N2-acyl groups on the stability of N-glycosidic bond and 2-amino group reactivity has been noted. The structure of a pyrimidine by-product (12) arising from the imidazole ring-opening of guaninium salt 4d in basic medium has been elucidated by 2D NMR.
Abstract: N9- and N7-Substituted (guaninyl)acetic esters were studied by electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry (ESI-MS/MS) in order to determine their ratio in alkylation reactions. The loss of ammonia is significantly different for the N9- and N7-alkylated guanine regioisomer pairs. More importantly, the abundance of the [MH-17]+ ion is in linear correlation with the N9-isomer content. Therefore, the ratio of regioisomers can be determined in a mixture containing these compounds.
2004
P. Pádár, G. Kovács and L. Kovács (2004): 6-[(4-Methoxybenzoyl)amino]-9H-purin-9-ylacetic acid. Molbank, M381-M381. Full text available as an html file
L. Kovács, P. Forgó, Z. Kele and é. Klement (2004): 2,2,2-Trichloro-1,1-dimethylethyl 4-tert-butylbenzoate. Molbank, M380-M380. Full text available as an html file
L. Kovács, P. Forgó and Z. Kele (2004): 2,2,2-Trichloro-1,1-dimethylethyl 4-methylbenzoate. Molbank, M379-M379. Full text available as an html file
L. Kovács, P. Forgó, Z. Kele and é. Klement (2004): 2,2,2-Trichloro-1,1-dimethylethyl bromoacetate. Molbank, M378-M378. Full text available as an html file
2003
Abstract: Sensitivity of ESI-MS analysis of crude PNA is enhanced using their pyridinium or thiazolium derivatives. Identification of molecular ion of the product is easier when the label contains bromine, based on the isotope distribution. Study of side reactions, occured upon the synthesis and/or cleavage, is simple with labelling. Sequencing of non-polar peptides is clear as only an type ions can be observed during their MS/MS analysis.
Abstract: The synthesis of free 5'-thiol-modified oligonucleotides using 4,4',4"-trimethoxytrityl (TMTr)-protected linker and standard Poly-PakTM purification has been described.
2002
Abstract: The optimization of PNA oligomer synthesis has been accomplished employing Fmoc/acyl-protected monomers on TentaGelTM and Wang resins. Among the tested activating agents (CMP, BET, HATU) the latter was of choice in solid phase syntheses. “Leakage” of TentaGelTM resin greatly hampers the solution and MS analyses. Synthesis and acyl group deprotection was separately examined using Wang resin. Optimal conditions also worked well on the CPG support. HPLC and MS analyses of the PNA oligomers were carried out under various conditions.
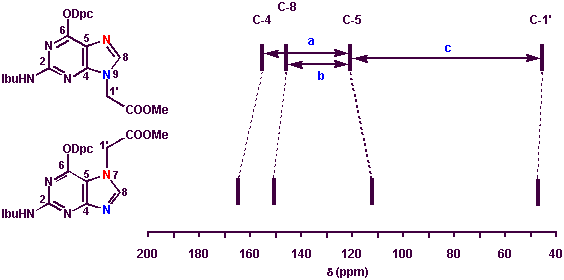
Abstract: 15N NMR chemical shifts of N7- and N9-purine derivatives were investigated systematically at natural abundance level of the 15N isotope. The NMR chemical shifts were determined and assigned using GSQMBC, GHMBC, GHMQC, and GHSQC experiments in solution. 15N cross-polarization magic angle spinning data were recorded for selected compounds in order to study the principal values of 15N chemical shifts. Geometric parameters obtained by using RHF/6-31G** and single-crystal X-ray structural analysis were used to calculate the chemical-shielding constants (GIAO and IGLO) which were then used to assign the nitrogen resonances observed in solid-state NMR spectra and to determine the orientation of the principal components of the shift tensors.
2001
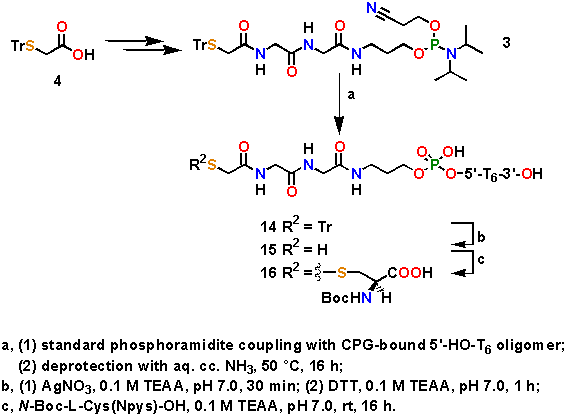
Abstract: A new, crystalline 5'-thiol modifier phosphoramidite monomer (3), available from S-tritylmercaptoacetic acid (4) in several steps and suitable for DNA synthesis, has been prepared. This monomer has been built into an oligonucleotide using the standard protocol. After cleavage, purification and removal of the trityl group with Ag+, a free 5'-thiol terminal oligonucleotide (15) has been obtained which was subsequently coupled to a cysteine derivative via a disulfide bridge to afford conjugate 16.

Gy. Kovács, Z. Kele, P. Forgó, L. Kovács (2001): 2-Bromo-3-ethylthiazolium tetrafluoroborate. Molecules, 5, M219. Full text available as an html file
2000
Z. Timár, L. Kovács, G. Kovács and Z. Schmél (2000): Fmoc/acyl protecting groups in the synthesis of polyamide (peptide) nucleic acid monomers. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1, 19-26.
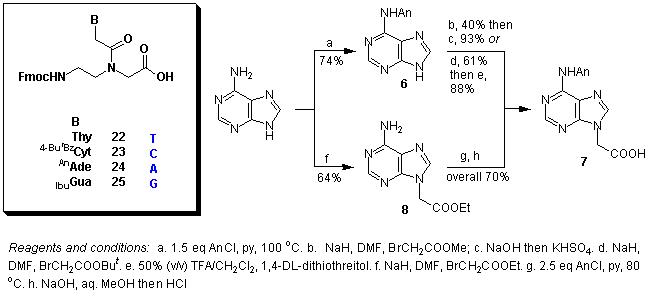
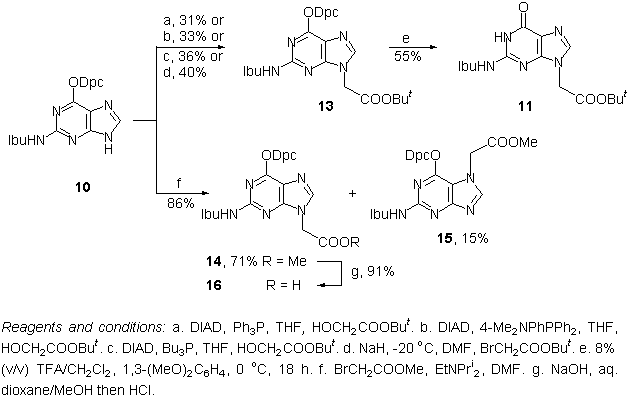
Abstract: The chemical synthesis of polyamide (peptide) nucleic acid (PNA) monomers 22-25 has been accomplished using Fmoc [N-(2-aminoethyl)glycine backbone], anisoyl (adenine), 4-tert-butylbenzoyl (cytosine) and isobutyryl/N,N-diphenylcarbamoyl (guanine) protecting group combinations. An alternative way for the preparation of (N6-anisoyladenin-9-yl)acetic acid 7 is described using partial hydrolysis of a dianisoylated derivative. For guanine alkylation different methods were studied including a) Mitsunobu reaction; b) low-temperature, sodium-hydride- and c) N,N-diisopropylethylamine-mediated alkylation reactions to give preferentially N9-substituted derivatives. The site of guanine alkylation was verified using HMQC and HMBC techniques. Empirical rules are proposed for differentiating N9/N7-substituted guanines on the basis of their 13C NMR chemical shift differences.
L. Kovács (2000): Unexpected Thorpe reaction of an a-alkoxynitrile. Molecules, 5, 127-131. Full text available as a pdf file
Zoltán Kupihár, Zoltán Schmél and L. Kovács (2000): 6-S-Trityl-mercapto-hexan-1-ol. Molecules, 5, M144. Full text available as an html file
L. Kovács and Péter Forgó (2000): Ethyl 2-(n-butylamino)-7-hydroxy-5-methylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-3-carboxylate. Molecules, 5, M143. Full text available as an html file
L. Kovács (2000): 1-(6-Amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-3-diazoacetone. Molecules, 5, M130. Full text available as an html file
1999
Z. Kele, Z. Kupihár, L. Kovács, T. Janáky and P. T. Szabó (1999): Electrospray mass spectrometry of phosphoramidites, a group of acid-labile compounds. J. Mass Spectrom., 34, 1317-1321.
Abstract: In contemporary solid-phase synthesis of oligonucleotides, phosphoramidites containing O-b-cyanoethyl and N,N-diisopropyl groups are the most widespread monomer units. The N,N-diisopropyl phosphoramidite group can be activated by mild acidic treatment which then easily reacts with nucleophiles (alcohols, water etc.) to furnish the requested phosphodiester linkage efficiently and cleanly. Due to the above-mentioned properties these compounds can not be investigated using the common ESI-MS technique. Their analytical characterization is further hampered by the fact that these compounds are very often transiently protected with acid-sensitive groups (4,4'-dimethoxytrityl, 4-monomethoxytrityl or trityl) which give quite intense signals in the spectra. Nanoelectrospray measurements from nonaqueous solvents (e.g. acetonitrile, methanol, tetrahydrofuran) were carried out in order to eliminate the nucleophilic water. Different types of alkali metal salts were used to form quasi molecular ions. Among these salts lithium chloride was found to be the most suitable for analysis of amidites. Quite intense [M+Li]+ and [M+Cl]- ions are formed in positive and negative ion mode, respectively. These ions were the base peaks in most cases and the intensities of the peaks, corresponding to the protecting group, were reduced by about 20 %. This method gives a powerful tool for mass spectrometric identification of phosphoramidites.
Z. Timár, S. Bottka, L. Kovács and B. Penke (1999): Synthesis and preliminary thermodynamic investigation of hypoxanthine-containing peptide nucleic acids. Nucleosides Nucleotides, 18, 1131-1133.
L. Kovács, Z. Timár and B. Penke (1999): Synthesis of peptide nucleic acid monomers. Nucleosides Nucleotides, 18, 727-729.
1998
E. Farkas, K. Megyeri, L. Somsák and L. Kovács (1998): Interaction between Mo(VI) and siderophore models in aqueous solution. J. Inorg. Biochem., 70, 41-47.
Abstract: A series of dihydroxamic acids (HORNOC-(CH2)n-CONROH, where if R = H - then n = 2, 5-7 and if R = CH3- then n = 4, 5) and two new dihydroxamate-based siderophore models, hexanedioic acid bis (3-hydroxycarbamoyl-methyl)amide (DhaI) and hexanedioic acid bis(3-hydroxycarbamoyl-propyl)amide (DhaII) have been characterized in terms of chelating properties toward molybdenum(VI). For comparison, the molybdenum(VI)-acetohydroxamic acid (Aha) and molybdenum(VI)-aminohydroxamic acid systems have also been studied. Potentiometric and spectrophotometric studies at ionic strength of 0.2 mol/dm3 (KCl) and at 25 C have been performed and the equilibrium constants have been determined. It has been found, that of the dihydroxamic acids, only the DhaI and DhaII form water soluble complexes with molybdenum(VI). Polynuclear complexes most probably precipitate with the other dihydroxamic acids. Complexes are formed up to ca. the neutral pH in all systems. Above this pH MoO42- and the free ligands exist. Although, very stable complexes are formed especially with DhaII, none of the studied ligands form a single bis(hydroxamato)dioxomolybdenum(VI) species. Mono(hydroxamato) trioxomolybdenum(VI) species are also formed, containing the uncoordinated moiety of the DhaI or DhaII in its protonated form. Out of aminohydroxamic acids, the b-alaninehydroxamic acid (b-Alaha) shows "Aha-like" coordination properties as the glutamic acid-g-hydroxamic acid (Glu-g-ha) does. The small differences with this latter ligand are possibly due to weak coordination of the carboxylate which makes the mono(hydroxamato)trioxomolybdenum(VI) species more stable and the uncoordinated carboxylates in bis(hydroxamato) dioxomolybdenum(VI) can protonate below pH 3. The tridentate coordination mode of aspartic acid-b-hydroxamic acid (Asp-b-ha) via the hydroxamate and carboxylate oxygens results in the formation of a dinuclear complex, [Mo2O5(LH)2]2- in addition to [MoO3(LH)]- (the protons are on the amino groups) in the pH-range 2.5-7.0.
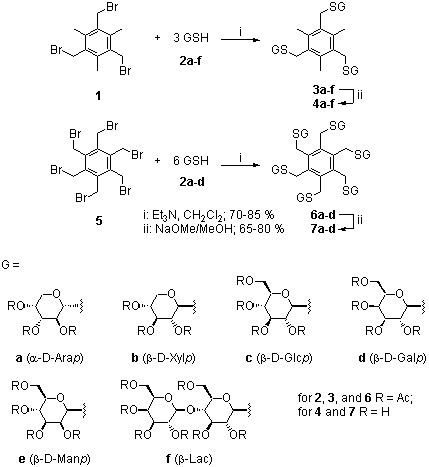
P. Herczegh, Á. Kovács-Kulyassa, G. Erdõsi, L. Kovács, T. Menyhárt, P. T. Szabó and J. Környei (1998): Thioglycosidic carbohydrate podands. Carbohydr. Lett., 3, 59-64.
Abstract: Reaction of tris- and hexakisbromomethylbenzenes 1 and 5 with 1-thiosugars and subsequent Zemplén deacetylation resulted in a new type of carbohydrate clusters (4a-f, 7a-d). 99mTc-complexing properties of 3c and 7c were determined under in vitro and in vivo conditions.
1997
L. Kovács (1997): A szénhidrátkémiai nómenklatúra problémái. Magy. Kém. Foly., 103, 178-183. [Problems of carbohydrate nomenclature (in Hungarian)].
Abstract: The present paper deals with the current problems of International and Hungarian carbohydrate nomenclature (naming novel cyclic forms, multiple configurational prefixes, triple or cumulated double bonds, carbohydrate phosphorus and uronic acid derivatives, lack of unified stereochemical representation styles; in Hungarian: the u/ü problem in the name of parent monosaccahrides, the -it/-itol suffix in the name of alditols, the designation of deoxy and halogenated compounds, naming compounds with non-contiguous stereocenters using configurational prefixes) and recommends methods for their solution.
1996
L. Kovács (1996): A sztereokémiai ábrázolásmódról. Magy. Kém. Foly., 102, 451-459. [On stereochemical notation (in Hungarian)].
Abstract: The paper treats the general aspects of stereochemical structure representation styles covering the rules associated with the Fischer and extended (and related) projections, and the advantages and drawbacks of their applications, with special regard to carbohydrates, are given. The general use of extended and Mills structures is recommended.
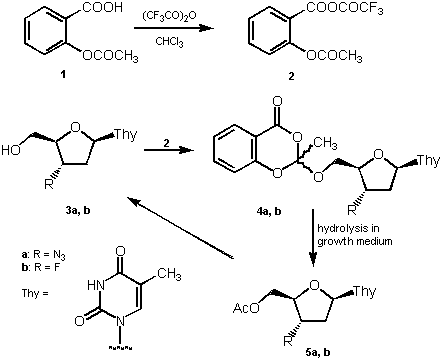
M. A. Zahran, L. Kovács, I. El Sakka, E. B. Pedersen and C. Nielsen (1996): The potential of aspirin in prodrug synthesis: a new potential delivery system of AZT and FLT. Arch. Pharm., 329, 417-420.
Abstract: Aspirin (O-acetylsalicylic acid, 1) has been used to synthesize prodrugs of 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine (AZT, 3a) and 3'-deoxy-3'-fluorothymidine (FLT, 3b). The mixed anhydride (2) between aspirin and trifluoroacetic acid was synthesized and reacted with AZT and FLT to give the blocked nucleosides (4a and 4b) attached through the 5'-position to the 2'-position of 2-methyl- 4H-1,3-benzodioxin-4-one. Hydrolysis of the synthesized prodrugs in the growth medium, used for the anti-HIV investigations, resulted in formation of 5'-O-acetylated drugs (5a and 5b) which were subsequently hydrolized into the original drugs.
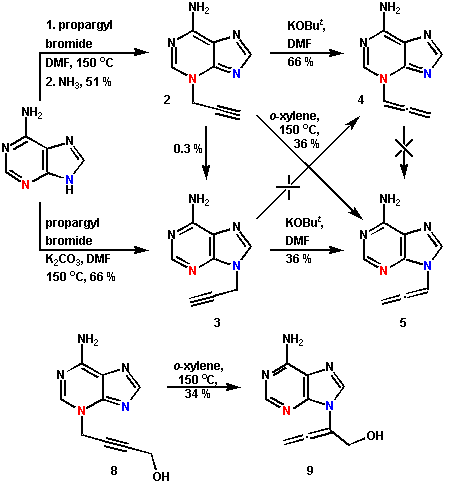
L. Kovács, G. Kiss, P. Benke and G. Pócsfalvi (1996): [3,3] Sigmatropic rearrangement of 3-alkynyladenines. Acta Chem. Scand., 50, 466-468.
Abstract: We have found in systematic investigations that 3-propargyladenine (2) undergoes a thermal [3,3] sigmatropic rearrangement to give 9-allenyladenine (5) whereas alkyl migration and isomerisation can be excluded. This was corroborated both experimentally, using 3-(4-hydroxy-2-butyne-1-yl)adenine (8), which rearranged to 9-(1-hydroxy-2,3-butadiene-2-yl)adenine (9), and by semiempirical calculations (AM1) as well as by intermediate analysis (RAIN).
1995
L. Kovács (1995): Thiazole C-nucleosides V. Remote group participation operating in the reactions of diastereomeric 2-(2'-deoxypent-1'-enopyranosyl)thiazoles. Bull. Soc. Chim. Fr., 132, 1015-1019.
Abstract: The supposed interplay of remote group participation and anomeric, allylic and stereodirecting effects exerted by different groups are invoked to explain the formation of a new stereocenter in unsaturated thiazole C-nucleosides 5 and 6.
1993
L. Kovács (1993): Methods for the synthesis of a-keto esters. Recl. Trav. Chim. Pays-Bas, 112, 471-496.
Abstract: This review article summarizes the main synthetic methods for the preparation of the title compounds from the period of 1980 to 1992 and is based on 363 research papers. The principal methods include C-C bond formation (C1, C2, C3, C4, two or three C1 synthons etc.) and functional group transformation reactions (oxidation of a-hydroxy esters, a-amino esters, esters and lactones, b-keto esters and their derivatives, alkynes etc.). All methods have been extensively illustrated (95 schemes).
1992
L. Kovács, M. Hesse (1992): Synthetic analogues of naturally occuring spider toxins. Helv. Chim. Acta, 75, 1909-1924.
Abstract: Naturally occurring spider toxins are potent inhibitors of glutamate receptors of the central nervous system and have the general structure (hetero)acyl → aminoacyl(I) → polyamine ← aminoacyl(II) (the arrow indicates the direction of an amide linkage). In the present paper the synthesis of ten spider toxin analogues (1-10) is reported. These compounds differ in their subunits and, in some cases, in the sequence of these moieties.
| Compd number | Structure | Abbreviations used |
| 1 | Iaa → Ala → Dhx ← Ac | Iaa- = (1H-indol-3-yl)acetyl;
Iaa(4-/5-OH)- = 4-/5-hydroxy-(1H-indol-3-yl)acetyl; Ipa- = (1H-indol-3-yl)propionyl; Ala- = alaninyl; -Dhx- = 1,6-diiminohexane; -Dpr- = 1,3-diiminopropane; Ac- = acetyl; Lys- = lysinyl; Trm- = N-substituted triptamine Ahx- = 6-aminohexanoyl residue. Arrows (→ and ←) are used to indicate the direction of the amide linkage. In this sense, acetyl group was considered to be an aminoacyl residue (Ac → and ← Ac) |
| 2 | Iaa → Ala → Dpr ¬ Ac | |
| 3 | Iaa(5-OH) → Ala → Dhx ← Ac | |
| 4 | Iaa(4-OH) → Ala → Dhx ← Ac | |
| 5 | Iaa → Ala → Dhx ← Lys × 2 HCl | |
| 6 | Iaa(5-OH) → Ala → Dhx ← Lys × 2 HCl | |
| 7 | Iaa(4-OH) → Ala → Dhx ← Lys × 2 HCl | |
| 8 | Ipa → Ala → Dhx ← Lys × 2 HCl | |
| 9 | Iaa → Dhx ← Ala ← Lys × 2 HCl | |
| 10 | Trm ← Ala ← Ahx ← Lys × 2 HCl |
1991
L. Kovács, P. Herczegh, G. Batta and I. Farkas (1991): Thiazole C-nucleosides IV. An entry to pent-1'-enopyranosylthiazole derivatives. Tetrahedron, 47, 5549-5560.
Abstract: Starting from ethyl 2-(3',4'-di- O-acetyl-2'-deoxy-L-erythro- or -D-threo-pent-1'-enopyranosyl)thiazole-4-carboxylate (1, 2) the synthesis of variously functionalized pent-1'-enopyranosylthiazoles 4-11, 15-20) was carried out with different O-, C-, S-, N-, and H-nucleophiles in the presence of Lewis acids. The regio- and stereoselective reactions proceeded with the Lewis acid-mediated formation of a carbocation (I) and the stereochemistry of the incoming nucleophile was determined by the neighbouring 4'-acetoxy group. However, with trimethylsilyl cyanide a 2',3'-unsaturated 1'-C-cyano derivative (26) was formed. The configuration and conformation of prepared unsaturated compounds was thoroughly studied and the presence of a conformational equilibrium 4H5 <-> 5H4 was deduced.
L. Kovács, P. Herczegh, G. Batta and I. Farkas (1991): Thiazole C-nucleosides III. Synthesis of pyranose analogues of tiazofurin. Tetrahedron, 47, 5539-5548.
Abstract: A large-scale synthesis of 3,4,5-tri-O-acetyl-2,6-anhydro-L-mannono- and -D-gulonothioamides (5, 6) has been achieved from the corresponding nitriles. The Hantzsch-reaction of 5 or 6 with ethyl bromopyruvate afforded the expected thiazoles (7, 8) only in a low yield along with furan derivatives (9-11), the formation of which is rationalized by an acid-catalysed rearrangement-elimination process. Attempted dehydration of 16 or 17 with trifluoroacetic anhydride/pyridine resulted in the formation of pent-1'-enopyranosylthiazoles (18-20). Deprotected thioamides (24, 25) furnished with ethyl bromopyruvate thiazoles (27, 28). The obtained thiazole esters (7, 8, 18-20, 27, 28) were transformed into new tiazofurin analogues (12, 13, 21-23).
1990
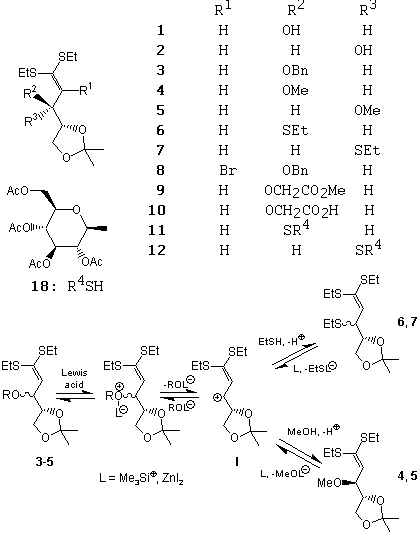
L. Kovács, P. Herczegh, G. Batta and I. Farkas (1990): Reactions of 2-deoxy-4,5-O-isopropylidene -D-erythro- and -D-threo-pent-1-enose diethyl dithioacetal derivatives. J. Carbohydr. Chem., 9, 585-599.
Abstract: The reactivity of the title compounds has been studied toward different nucleophiles and electrophiles. Unlike other ketene dithioacetals, compounds 3-5 did not add nucleophile to the double bond. Instead, in the presence of Lewis acids they underwent substitution reaction at position 3. If the nucleophile was not strong enough, formation of 6 and 7 were observed. With 2,3,4,6-tetra-O-acetyl-1-thio- b-D-glucopyranose (18), a 3:1 mixture of diastereomers 11 and 12 was formed from 4. These observations may be interpreted in terms of easy formation of the allylic carbocation I which gives diastereomers with nucleophiles. However, this allylic ether-like behaviour was ruled out by the fact that compounds 9 and 10 did not undergo [2,3] sigmatropic rearrangement with lithium diisopropylamide. With N-bromosuccimide compound 3 gave the 2-bromo derivative 8. Compounds 3 and 8 resisted common mercury salt assisted demercaptalisation procedures.
1989
P. D. Nagy, R. Gáborjányi, L. Kovács and I. Farkas (1989): Antiviral activity of tiazofurin against barley stripe mosaic virus. Antiviral Res., 11, 41-45.
Abstract: Tiazofurine (2-b-D-ribofuranosylthiazole-4-carboxamide) was found to inhibit replication of barley stripe mosaic virus (BSMV) in barley and wheat plants. Treatment with this nucleoside analogue delayed and inhibited symptom development and suppressed virus multiplication. The most effective concentration applied twice as a foliar spray 3 h and 1 day after inoculation, was 10-3 M. Decreased virus multiplication was obtained without marked phytotoxicity. Three weeks after the treatment the antiviral effect declined.
1987
L. Kovács, P. Herczegh, G. Batta and I. Farkas (1987): Two acyclic analogues of 2-b-D-ribofuranosylthiazole-4-carboxamide (tiazofurin). Heterocycles, 26, 947-960.
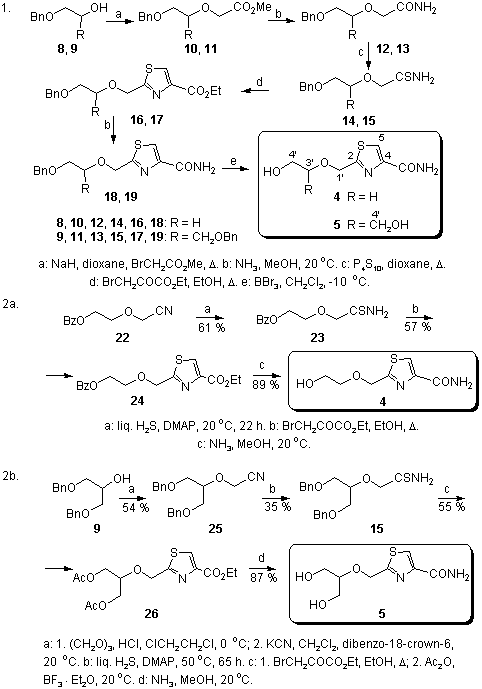
Abstract: Two different synthetic strategies have been elaborated for the synthesis of 2-[(2-hydroxyethoxy)methyl]thiazole-4-carboxamide (4) and 2-{[2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethoxy]methyl}thiazole-4-carboxamide (5).
1986
L. Kovács, P. Kerekes (1986): Sintezo de nova alkaloido: kristadino. Sci. Komun. (Budapest), 8-11. [Synthesis of a new alkaloid: cristadine (in Esperanto)]. For the abstract of this paper see the next article.
1985
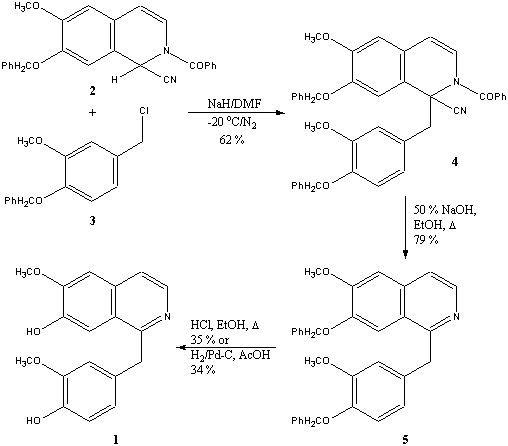
L. Kovács, P. Kerekes (1985): Synthesis of alkaloids using Reissert compounds V. Synthesis of 1-(4'-hydroxy-3'-methoxybenzyl)-7-hydroxy-6-methoxyisoquinoline (cristadine). Acta Chim. Hung., 120, 103-105.
Abstract: Using the appropriate Reissert compound (2) and substituted benzyl halide (3), the total synthesis of a new benzylisoquinoline alkaloid, cristadine (1) has been achieved, conclusively proving its structure.
1999-